What is automation?
Automation is the development and use of technology to create and provide goods and services with little or no human involvement. Many tasks that were previously carried out by people are now more effective, dependable, and quick because of the use of automation technologies, techniques, and procedures.
In many different industries, including manufacturing, transportation, utilities, defense, buildings, operations, and most recently, information technology, automation is widely used.
Technology is used in business process automation to simplify operational procedures. An automation will carry out a procedure so that you don’t have to use a specific trigger or action.
Why automation is important?
Typically, automation is employed to reduce labor-intensive tasks or to replace people in other boring or repetitive jobs. Automation can be found in almost all industries and market segments, but it is more common in the manufacturing, utility, transportation, and security sectors.
For example, robotic assembly lines are used in the majority of manufacturing facilities as an automated procedure. Only the procedures need to be defined and overseen by humans; the machines, which automatically transform raw materials into completed goods, are in charge of assembling the various components.
The impact of automation in the tech sector is growing quickly, both in the software/hardware and machine layers. The use of a new artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies is now boosting the field’s evolution.
There are many different automation solutions available such as:
• Business Process Automation
• Robotic Process Automation
• Intelligent Process Automation
• IT Automation
• Machine Learning
• Deep Learning
Examples of automation
In the field of information technology, a software script can test the software and generate a report. Additionally, there are numerous software solutions on the market that may produce code for an application. Users merely need to specify the process and configure the tool.
Another emerging type of high-quality automation is advanced business intelligence into applications. Automation has substantially boosted productivity in various industries in recent decades, saving time and money.
From the most basic to the most complex applications, automation can be found in many parts of daily life. Common examples include:
Cybersecurity:
When AI (Artificial Intelligence) and automation are used together, security is where they truly show their full potential. To prevent future breaches, advanced systems can educate themselves and learn from human behavior as well as prior attacks.
Home automation:
Home automation is a network of hardware, communication, and electronic interfaces that use the Internet to connect common devices. This lets you to turn on the lights, lock the front door, or even turn down the heat from wherever you are.
Customer Service:
Businesses can utilize automation to automate responses to clients, and then use user data to create more personalized responses. This enables businesses to reply to clients not only quickly, but also in a highly personalized manner.
Office automation:
When you first hear the term “office automation,” you might picture robots performing human tasks. However, this is not the case. Office automation is a procedure that combines tools to automate information gathering, collaboration, presentation, and calculation.
Decision Automation:
Decision Automation is a practice that automates decision-making processes across organizations by utilizing various techniques and technologies such as AI/ML, Business Rules, Multistep Decisions, Orchestration, Decision Robotics, and so on.
Data center automation:
The majority of data center automation is distributed through software solutions that allow access to centralized resources. This enables the servers, storage, networks, and other functions to be automated.
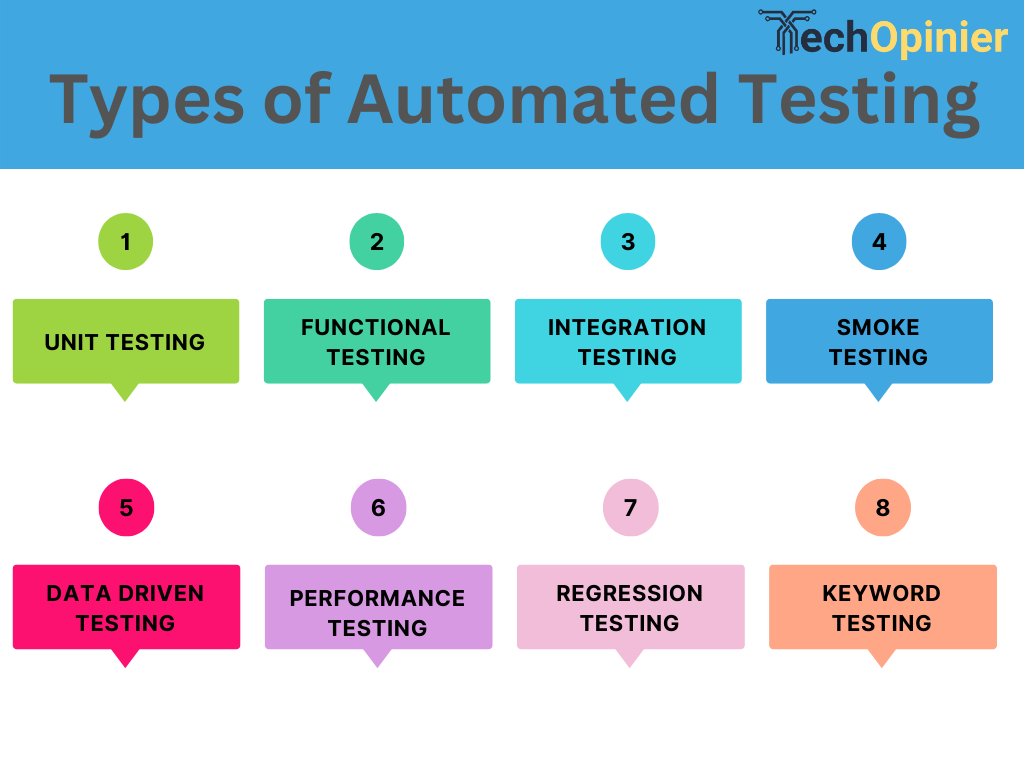
Test automation:
Software code is tested for quality assurance (QA) by scripts and other automation tools. Test automation enables development teams to build, test, and release software more quickly and reliably.
Benefits of automation
Automation can greatly enhance busy lives. Automation is not always intended to replace workers. The focus and benefits are on productivity, consistency, and efficiency, but some of it will come as a result of eliminating procedures that demand human interaction.
While automated technology may appeal to people on an emotional level, it is also quite practical. Since automated technology frequently reduces human mistake, actions are frequently carried out in a safe and efficient manner.
IT operations managers battle every day to do more work with fewer staff members. To assist them streamline IT operations, IT automation provides a variety of benefits including:
Reducing Operational Costs
By automating repetitive tasks effectively such as application deployment and product delivery, change and delivery management, and software updates, IT operations can save money by working more effectively, making fewer errors, and decreasing manpower.
Greater Productivity
Workflow automation reduces manual work, including manual testing, increasing output and freeing up personnel to focus on more critical initiatives. Furthermore, employees can accomplish more work each day.
Ensuring High Availability
High availability is definitely one of the major aims of IT administration. Automated processes can be useful in this situation as well. A disc drive may fail, but the problem becomes serious when there is no suitable backup—or, worse, when the backup cannot be retrieved.
The ability to automate your save and recovery processes to ensure protection from the possible disaster of data loss or accidental harm to data structures due to human error is a key advantage of automation.
Better Reliability
By removing the human factor from tedious, repetitive work, automation reduces costly errors. This is especially useful in wide area networks with a variety of operating systems. Managers of IT operations can significantly increase the reliability and free staff members from tedious manual tasks by automating repeated business procedures.
Optimizing Performance
IT operations managers are not only expected to accomplish more work, but also to complete it more swiftly and effectively. Without having to hire extra people, they can increase performance with the use of IT automation technologies.
Takeaway:
Automation is the use of computer programs to carry out operations that would normally be handled by humans. Automation can result in significant cost savings, both directly and indirectly. The majority of people consider automation to be cost-effective when they talk about cutting down on labor hours needed to perform activities and increasing staff productivity.
However, it also ensures consistency, reduces errors (saving additional staff time normally spent on damage control), improves resource utilization (helping to save on infrastructure costs), and even helps save on security costs by preventing costly data breaches.
Hire the best automation experts here.

